Introduction
In recent years, probiotics have gained significant attention in the health and wellness community. Often referred to as “good” or “friendly” bacteria, probiotics are live microorganisms that provide numerous health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. This article will explore the definition, benefits, sources, types, and potential side effects of probiotics, helping you understand why they are essential for maintaining gut health and overall wellness.
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms, primarily bacteria and yeasts, that confer health benefits to the host when taken in sufficient quantities. These beneficial organisms play a crucial role in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome, which is essential for optimal digestive health and immune function.
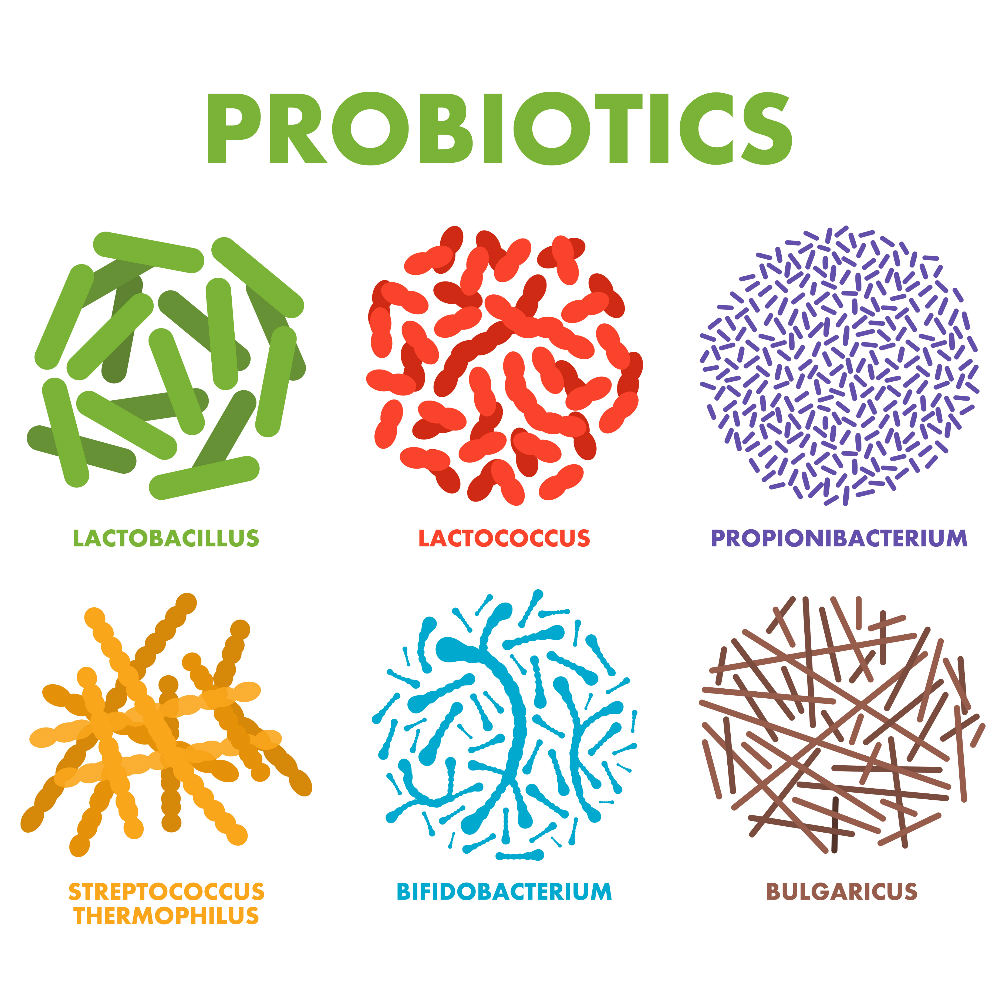
The most common strains of probiotics belong to the Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium genera. However, other microorganisms, such as Saccharomyces boulardii (a type of yeast), also fall under the umbrella of probiotics.
Benefits of Probiotics
Probiotics offer a wide array of health benefits, including:
- Improving Digestive Health: Probiotics help restore the natural balance of gut bacteria, which can be disrupted by factors such as antibiotics, poor diet, and stress. They can alleviate symptoms of digestive disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diarrhea, and constipation.
- Boosting Immune Function: A healthy gut microbiome plays a critical role in immune health. Probiotics can enhance the production of antibodies and promote the activity of immune cells, helping to fend off infections and illnesses.
- Preventing Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea: Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to diarrhea. Probiotics have been shown to reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhea by replenishing beneficial bacteria.
- Supporting Mental Health: Emerging research suggests a link between gut health and mental well-being. The gut-brain axis refers to the communication between the gut and the brain. Probiotics may help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression by influencing neurotransmitter production.
- Enhancing Nutrient Absorption: Probiotics can improve the absorption of nutrients, including vitamins and minerals. They help break down food particles, making it easier for the body to utilize essential nutrients.
- Promoting Healthy Skin: Some studies suggest that probiotics may benefit skin health by reducing inflammation and combating skin conditions like eczema and acne.
Sources of Probiotics
Incorporating probiotics into your diet can be achieved through various food sources and supplements. Here are some popular options:
- Fermented Foods: Fermented foods are rich in probiotics and can be easily included in your diet. Some examples include:
- Yogurt: A well-known source of probiotics, yogurt contains live cultures that can promote gut health.
- Kefir: A fermented dairy product similar to yogurt but thinner in consistency, kefir is packed with probiotics and beneficial yeasts.
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage that is rich in probiotics and can be enjoyed as a side dish or topping.
- Kimchi: A spicy Korean dish made from fermented vegetables, kimchi is not only flavorful but also a great source of probiotics.
- Miso: A traditional Japanese seasoning made from fermented soybeans, miso can be used in soups, dressings, and marinades.
- Tempeh: A fermented soybean product that serves as a protein-rich meat alternative, tempeh contains probiotics as well.
- Probiotic Supplements: For those who may not get enough probiotics from food sources, supplements are an effective option. Available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders, it’s essential to choose a high-quality product with specific strains that target your health needs.
Types of Probiotics
Different strains of probiotics provide various health benefits. Here are some of the most researched and commonly used strains:
- Lactobacillus: This genus includes numerous strains that are effective for digestive health, lactose intolerance, and overall immune support.
- Bifidobacterium: Known for its role in maintaining gut health, this genus is particularly beneficial for infants and children.
- Saccharomyces boulardii: This probiotic yeast is effective in preventing and treating diarrhea, particularly antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
- Streptococcus thermophilus: Often found in yogurt, this strain helps improve lactose digestion and supports gut health.
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus: This strain is known for its immune-boosting properties and its ability to alleviate gastrointestinal disorders.
Potential Side Effects of Probiotics
While probiotics are generally safe for most people, some individuals may experience mild side effects, including:
- Gas and Bloating: Some people may experience increased gas and bloating when they first start taking probiotics. These symptoms typically subside as the body adjusts.
- Digestive Discomfort: Some individuals may experience mild digestive discomfort, especially if they consume large amounts of probiotic-rich foods or supplements.
- Infections: In rare cases, individuals with compromised immune systems or underlying health conditions may be at risk for infections due to probiotics.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any probiotic regimen, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
Choosing the Right Probiotic
When selecting a probiotic supplement, consider the following factors:
- Strain Specificity: Different strains provide different benefits. Choose a probiotic that contains strains suited to your specific health needs.
- Colony Forming Units (CFUs): Look for products with a sufficient number of CFUs. Generally, a probiotic supplement should contain at least 1 billion CFUs per serving for effectiveness.
- Shelf Stability: Check if the probiotic requires refrigeration. Some strains are more stable than others and can be stored at room temperature without losing potency.
- Expiration Date: Ensure the product is within its expiration date, as probiotics can lose potency over time.
- Quality and Certification: Choose products from reputable brands that adhere to good manufacturing practices and are tested for quality and potency.
Incorporating Probiotics into Your Diet
To reap the benefits of probiotics, consider the following tips:
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to probiotics, start with small amounts of fermented foods and gradually increase your intake. This approach allows your digestive system to adjust.
- Diversify Your Sources: Incorporate a variety of probiotic-rich foods into your diet to expose your gut to different strains and maximize benefits.
- Combine with Prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed probiotics and help them thrive in the gut. Foods like garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus are excellent sources of prebiotics.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key to maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Aim to include probiotics in your daily routine for lasting benefits.
Conclusion
Probiotics are a powerful tool for enhancing gut health and overall wellness. With their numerous benefits, including improved digestion, boosted immune function, and support for mental health, incorporating probiotics into your diet can lead to a healthier lifestyle. Whether through fermented foods or high-quality supplements, finding the right probiotics for your individual needs is essential. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure you make informed choices for your health.
By understanding probiotics and their role in maintaining gut health, you can take proactive steps toward a healthier, happier you.