Introduction
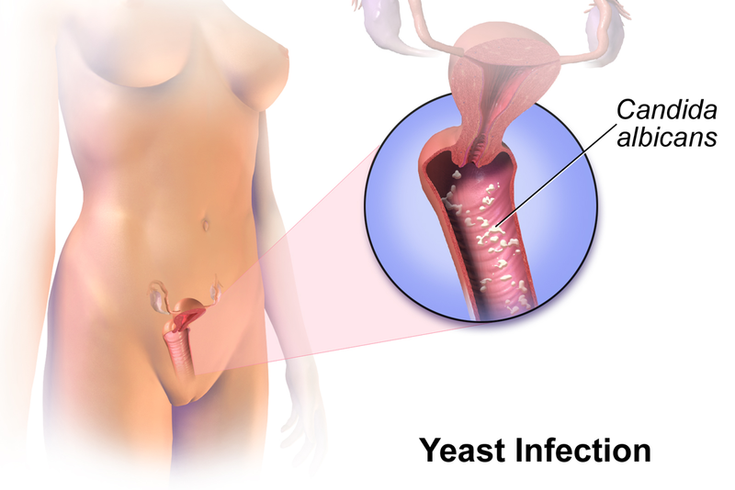
A yeast infection, clinically known as candidiasis, is a common fungal infection caused primarily by the overgrowth of Candida species, particularly Candida albicans. This condition affects millions of individuals worldwide and can occur in various parts of the body, most notably in warm and moist areas like the vagina, mouth, and skin folds. While yeast infections are typically not serious, they can cause significant discomfort and may indicate underlying health issues. Understanding the symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies for yeast infections is crucial for effective management and overall well-being.
What is a Yeast Infection?
A yeast infection occurs when the balance of microorganisms in the body is disrupted, allowing the naturally occurring Candida fungi to multiply uncontrollably. Under normal circumstances, the body maintains a delicate balance of bacteria and fungi, which helps to keep harmful organisms in check. However, various factors can contribute to an imbalance, leading to an overgrowth of Candida and the development of a yeast infection.
Types of Yeast Infections
- Vaginal Yeast Infections: This is the most common type of yeast infection, affecting many women at some point in their lives. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and can significantly impact quality of life.
- Oral Thrush: A yeast infection in the mouth, known as oral thrush, is characterized by white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and throat. It can cause discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
- Skin Yeast Infections: These occur in warm, moist areas of the body, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. Symptoms may include red, itchy rashes and cracked skin.
- Invasive Candidiasis: This is a more severe form of yeast infection that occurs when Candida enters the bloodstream and affects internal organs. It is more common in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Symptoms of a Yeast Infection
Symptoms of a yeast infection can vary depending on the affected area. Here are the most common signs and symptoms for different types of infections:
1. Vaginal Yeast Infection
- Itching and Irritation: Women often experience intense itching in the vaginal area, which can be quite uncomfortable.
- Discharge: A thick, white discharge resembling cottage cheese is a hallmark symptom. The discharge is typically odorless.
- Redness and Swelling: The vulva may become red and swollen, leading to further discomfort.
- Pain During Intercourse: Many women report pain during sexual activity due to irritation and inflammation.
- Burning Sensation: A burning sensation during urination can occur if the urine comes into contact with inflamed tissues.
2. Oral Thrush
- White Patches: Characteristic white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and sometimes the throat are the most visible symptoms.
- Soreness: The affected areas may become sore, leading to discomfort while eating or swallowing.
- Cottony Feeling: Some individuals describe a cottony feeling in the mouth.
- Loss of Taste: In some cases, oral thrush can lead to a temporary loss of taste.
3. Skin Yeast Infection
- Rashes: Red, itchy rashes can develop in warm, moist areas such as the groin, armpits, and under the breasts.
- Cracked Skin: Skin may crack, leading to discomfort and increasing the risk of secondary infections.
- Foul Odor: In some cases, the affected area may have a foul smell due to the overgrowth of yeast.
Causes of Yeast Infections
Understanding the causes of yeast infections is essential for prevention and management. Several factors can contribute to the overgrowth of Candida:
1. Antibiotic Use
Antibiotics are designed to kill harmful bacteria, but they can also disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms in the body. When beneficial bacteria are reduced, Candida can multiply unchecked, leading to a yeast infection. This is particularly common after a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
2. Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormone levels can create an environment conducive to yeast overgrowth. Common instances include:
- Menstruation: Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can affect the vaginal environment, making it more prone to yeast infections.
- Pregnancy: Increased estrogen levels during pregnancy can lead to a higher risk of yeast infections.
- Hormonal Therapies: Hormonal contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy can also influence the balance of flora in the body.
3. Weakened Immune System
Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or undergoing chemotherapy, are at a higher risk of developing yeast infections. A weakened immune system struggles to keep Candida growth in check.
4. High Sugar Diet
Yeast thrives on sugar. Diets high in refined sugars and carbohydrates can promote Candida overgrowth. Consuming large amounts of sugary foods can lead to a higher likelihood of developing a yeast infection.
5. Moist Environments
Warm, moist areas of the body provide an ideal environment for yeast to flourish. Factors contributing to moisture include:
- Damp Clothing: Wearing wet swimsuits or sweaty workout clothes for extended periods can increase the risk of yeast infections.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate hygiene practices, particularly in warm climates, can lead to an accumulation of moisture and promote yeast growth.
6. Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes, especially those with uncontrolled blood sugar levels, are more susceptible to yeast infections. High blood sugar levels can increase the sugar concentration in bodily fluids, providing a food source for yeast.
Diagnosis of Yeast Infections
If you suspect you have a yeast infection, it’s crucial to seek a diagnosis from a healthcare provider. The diagnosis may involve the following steps:
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination, particularly of the affected area, will be conducted. For vaginal infections, a pelvic exam may be necessary.
- Symptom Discussion: Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any recent antibiotic use.
- Laboratory Tests: Laboratory tests may include:
- Vaginal Swab: A sample may be taken from the affected area to identify the presence of Candida.
- Culture: A culture may be performed to determine the specific strain of yeast involved.
- Microscopic Examination: A sample may be examined under a microscope for yeast cells.
- Differential Diagnosis: It’s essential to differentiate yeast infections from other conditions with similar symptoms, such as bacterial vaginosis or sexually transmitted infections (STIs). This may involve additional testing.
Treatment Options for Yeast Infections
Treatment for yeast infections typically involves antifungal medications, which can be administered in various forms. Here are the most common treatment options:
1. Over-the-Counter Antifungals
Many mild yeast infections can be effectively treated with over-the-counter antifungal medications. These products are available in various forms, including:
- Creams and Ointments: Topical antifungal creams or ointments can be applied directly to the affected area.
- Vaginal Suppositories: These are inserted into the vagina and dissolve, releasing antifungal medication.
- Oral Tablets: Some over-the-counter options are available in oral tablet form.
Common active ingredients in over-the-counter antifungals include:
- Clotrimazole
- Miconazole
- Tioconazole
2. Prescription Antifungals
For more severe or recurrent infections, a healthcare provider may prescribe oral antifungal medications, such as:
- Fluconazole (Diflucan): This is a single-dose oral medication that is often effective for treating vaginal yeast infections.
- Itraconazole: Another oral antifungal that may be prescribed for resistant infections.
3. Home Remedies
Some individuals may prefer to explore home remedies for mild symptoms. While these remedies are not a substitute for medical treatment, they may provide relief for some:
- Probiotics: Probiotics may help restore the natural balance of flora in the body. Consuming yogurt with live cultures or taking probiotic supplements can be beneficial.
- Coconut Oil: Known for its antifungal properties, coconut oil can be applied topically to affected areas.
- Garlic: Garlic has natural antifungal properties and can be consumed or applied topically, although care should be taken to avoid irritation.
4. Preventative Treatments
For individuals who experience recurrent yeast infections, preventive strategies may include:
- Long-term Antifungal Treatment: A healthcare provider may recommend a longer course of antifungal medication or a low-dose oral antifungal taken periodically.
- Probiotic Supplementation: Regular use of probiotics may help maintain a healthy balance of flora and reduce the risk of future infections.
Managing Yeast Infections
In addition to medication, there are several strategies individuals can adopt to manage yeast infections effectively:
- Keep the Area Dry: Ensure that the affected area is clean and dry. After bathing, pat the area dry rather than rubbing it.
- Wear Loose Clothing: Opt for breathable fabrics and avoid tight-fitting clothing to reduce moisture buildup.
- Avoid Irritants: Steer clear of scented soaps, lotions, and douches that can irritate the genital area and disrupt the natural balance of bacteria.
- Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels: For individuals with diabetes, controlling blood sugar levels can help reduce the risk of yeast infections.
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and support overall health.
Preventing Yeast Infections
While it may not be possible to prevent all yeast infections, several strategies can significantly reduce the risk:
- Maintain Good Hygiene:
- Daily Cleaning: Clean the genital area daily with mild soap and water. Avoid harsh soaps and fragrances that can irritate the skin.
- Change Out of Wet Clothes Promptly: If you’ve been swimming or exercising, change out of wet clothing as soon as possible to reduce moisture buildup.
- Wear Breathable Clothing:
- Choose loose-fitting cotton underwear and avoid synthetic fabrics that can trap moisture.
- Opt for breathable fabrics for outerwear, especially in warm weather.
- Limit Sugar Intake:
- Reducing sugar and refined carbohydrate consumption can help keep Candida levels in check. Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Be Cautious with Antibiotics:
- Only take antibiotics when necessary, and consult your healthcare provider about taking probiotics to maintain a healthy balance of bacteria during and after antibiotic treatment.
- Practice Safe Sex:
- Using condoms can reduce the risk of infections, including STIs that may trigger yeast infections.
- Monitor Hormonal Changes:
- If you are prone to yeast infections related to hormonal fluctuations, discuss options with your healthcare provider to manage symptoms effectively.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent or Recurrent Yeast Infections: If you have four or more yeast infections in a year, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
- Symptoms That Don’t Improve: If over-the-counter treatments do not alleviate your symptoms within a few days, consult a healthcare provider.
- Severe Symptoms: Severe itching, swelling, or pain that interferes with daily activities warrants professional evaluation.
- Unusual Symptoms: If you experience unusual or severe abdominal pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Conclusion
A yeast infection is a common condition that can lead to discomfort and inconvenience. By understanding the symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies, individuals can effectively manage and reduce their risk of developing yeast infections. If you suspect you have a yeast infection, consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
With the right knowledge and support, you can navigate the challenges of yeast infections and maintain your overall health and well-being.